Nitro Quimica invests in eco-efficiency initiatives that factor sustainability aspects into our approach to innovation at our manufacturing plants. Sustainability attributes embedded in our products are a competitive differentiator and add further, long-term value to our resins and solutions
Facilities improvement projects delivered:
10% energy savings at our nitrocellulose plant
5% water savings
All environmental indicators are included as components of annually monitored corporate targets.
Water
The water we use in our production process is pumped directly from the Tiete river. Nitro Quimica’s manufacturing facilities use approximately 400 m3 of water per hour, which is carefully metered. The water from the Tiete River – infamous for its high levels of municipal pollutants – is treated on-site prior to use in our plants. At the nitrocellulose plants, water is reutilized in a number of processed before it becomes an effluent, reducing our consumption of filtered water. In the sulfuric acid process, industrial wastewater is further reutilized in a gas scrubber consuming 40 cubic meters of water per hour. With a focus on reducing water consumption, Nitro Quimica uses the Lean Six Sigma methodology to improve performance by eliminating waste.
Nitro Quimica’s water resources also include on-site artesian wells. All wastewater is pumped to a company-operated wastewater treatment plant. At the plant, wastewater undergoes primary treatment (pH adjustment and sludge removal) and quality control. Primary treatment is followed by a second, biological treatment stage at the municipal treatment plant. Following secondary treatment, part of the water returns to the river and part is recycled into the process. Our water discharge amounts to approximately 400 m3 per hour. G4-EN22
Water usage at Nitro Quimica
Conveyance water (40 m³/h): used in one of the stages of nitrocellulose production (digestion). The product is boiled and the water is drained and filtered before being pumped to a recycling system.
Scrubber in sulfuric acid process (72 m³/h): the sulfuric acid process incorporates a scrubber using water from the wastewater treatment plant (ETE).
Reverse osmosis (20 m³/h): in the water treatment process, part of the water that would otherwise be disposed of as wastewater is sent to the treatment plant for further use as plant water.
In recent years, the Company has reutilized an average of 15% of total water withdrawal (G4-EN8). Total reutilized water volumes in 2016 were 571,525 m³.
Total water withdrawal by source in m3
G4-EN8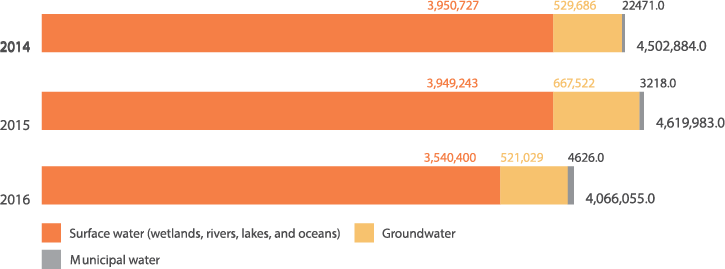
Water recycled and reused
G4-EN10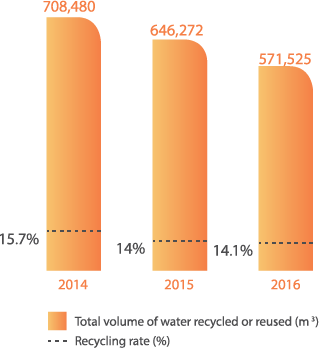
Total water discharge in m³
G4-EN22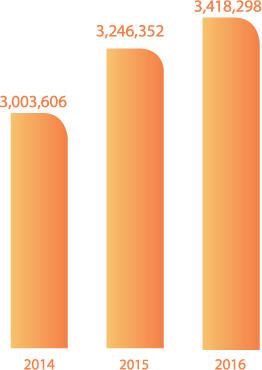
Emissions
G4-EN15, G4-EN16, G4-EN17The primary emissions from our operations are COX (carbon oxides) and SOX (sulfur oxides) from burning sulfur to produce sulfuric acid, and NOX (nitrous oxides) from the manufacture of nitrocellulose. While our emissions levels are below the regulatory limits required by the Sao Paulo State environmental regulator (CETESB), Nitro Quimica has established its own, more stringent emissions targets. SOX and emissions are monitored online in real time and reports are transmitted to the environmental regulator. In 2018 our sulfuric acid plant will migrate to a new technology that will reduce SOX emissions.
Nitro Quimica has prepared inventories of its scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions since 2014, using the Brazilian GHG Protocol Program platform. Scope 3 emissions are not measured due to the difficulty in tracking these omissions across the value chain. The possibility of extending our inventories to these emissions will be considered in 2017.
SOX and NOX emissions are monitored in real-time
Consumption of refrigerant gases at our manufacturing plant increased in 2015, resulting in higher volumes of fugitive emissions. Transportation emissions may have been affected as a result of our recently hiring a new trucking company.
Indirect greenhouse gas emissions (scope 1) by source in metric tons of CO2 eq.
G4-EN 15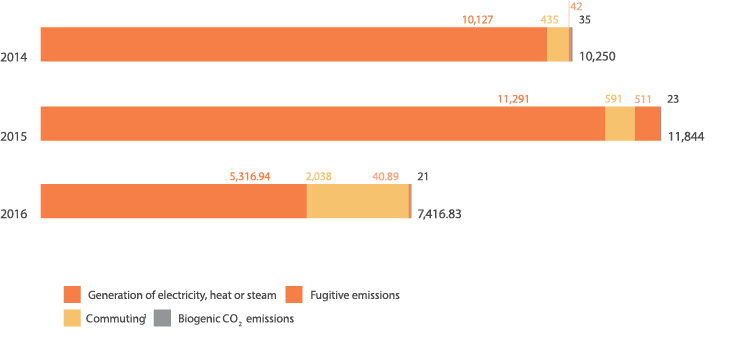
*Scope 1 – Emissions from sources that are owned or controlled by the organization.
1 Total emissions of materials, products and waste will also be included in 2017.
Indirect greenhouse gas emissions (scope 2) by source in metric tons of CO2 eq.
G4-EN 16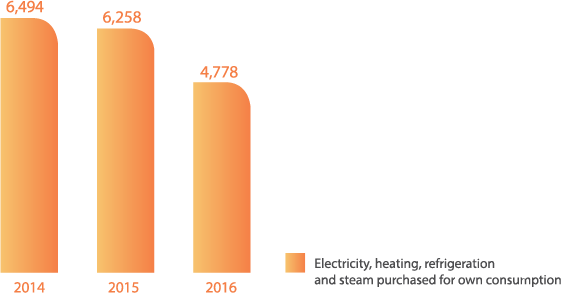
On-site power generation
We produce up to 40% of the electricity used at our plant from a small on-site co-generation thermal power plant. A turbine installed in the Utilities Plant uses steam from sulfur burning in the manufacture of sulfuric acid to generate electricity. In 2018, with the added capacity at the sulfuric acid plant, the proportion of electricity produced on-site should increase to 50%.
Direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions (scope 1 and 2) by source in metric tons of CO2 eq.
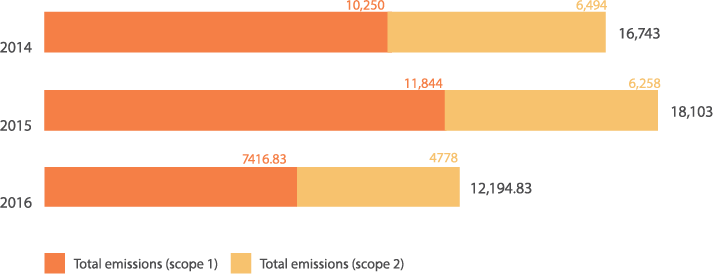
| Category | Emissions source | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx (ppm) | Nitric acid - nitrocellulose production process | 31,055 | 34,939 | 34,019 |
| SOx (t) | Sulfur combustion in the production of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) | 334 | 367 | 424 |
| COx (m3) | Natural gas combustion to produce steam (Boilers) | 9,618 | 10,639 | 3,747 |
NOX – Emissions measured by online analyzers at the outlet of the absorption column.
SOX – Emissions measured using stoichiometric calculations based on sulfuric acid output.
COX – Emissions measured based on annual combustion of natural gas using an emissions factor.
Waste Material
We continuously develop sustainable approaches to managing the waste streams we produce. Beginning in 2017, the sludge from our on-site wastewater treatment plant will be sent for composting at a partner firm. In this biological process, microorganisms transform the organic matter in the sludge into a compost fertilizer for agriculture. The sludge from water treatment was previously disposed of at a sanitary landfill.
Since 2016, our solvent waste streams from the manufacture of end products have been recycled by a partner firm into paint thinners and industrial cleaning solvents.
Nitro Quimica works with specialized firms to ensure the proper disposal of waste materials, and any hazardous waste is transported outside Company premises.
G4-EN23: Total weight of waste by type and disposal method
G4-EN25: Weight of hazardous waste transported
| Disposal method | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | Total waste disposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reutilization | 1,539 | 1,015 | 1,463 | Sulfur sludge and wood |
| Recycling | 181 | 290 | 496 | Paper, corrugated cardboard, plastic, scrap metal |
| Landfill | 2,029 | 1,743 | 2,013 | Construction waste, canteen waste, discarded nonhazardous products, sweeping waste, thermal insulation, wastewater treatment sludge |
| Total | 3,748 | 3,046 | 3,972 |
| Disposal method | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | Total waste disposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycling (calcination) | 2.26 | 31.41 | 0.60 | V2O5 catalysts, lamps and batteries |
| Reclamation | 11.1 | 15.0 | 3.2 | Used lube oil/burnt oil; solvents and resins |
| Incineration | 1.3 | 3.7 | 1.3 | Laboratory reagents, contaminated liquid waste |
| Co-processing | 15.4 | 19.8 | 11.9 | Miscellaneous contaminated solid waste |
| Total | 30.06 | 69.91 | 17 |
